As of July 2022, we have the possibilty to execute web service operations as idempotent operations.
The article Making retries safe with idempotent APIs explains it perfectly. I had already thought of this solution before searching the internet for best practices to this problem. From that article, I would emphasize:
- our preferred approach is to incorporate a unique caller-provided client request identifier into our API contract. Requests from the same caller with the same client request identifier can be considered duplicate requests and can be dealt with accordingly.
- we can ignore
- Semantic equivalence and support for default retry strategies
- Late arriving requests and the life span of unique client request identifiers
- Responding when a customer changes request parameters on a subsequent call where the client request ID stays the same
Supported Operations
The exact list of supported operations can be obtained by executing this SQL command in the database:
SELECT name FROM vtiger_ws_operation where is_idempotency=1
As of the moment of writing this article, they are:
- create
- CreateWithValidation
- update
- UpdateWithValidation
- revise
- ReviseWithValidation
- upsert
- MassCreate
- MassUpdate
- convertlead
- ExecuteWorkflow
- executeBusinessAction
- addProductImages
How to define a web service operation as idempotent
To mark a supported operation as idempotent we have to send an additional parameter with the call: cbwsOptions. This parameter is an array in which we can define the ClientRequestIdentifier. This option can have two values:
generateor empty: in this case, coreBOS will generate the ID for the operation so it can do the tracking of the repeated calls internally- any string identifier for the operation. If the ID is present in the application, it will consider the operation as repeated and return the previous result, if not, it will use the given ID as the idempotent identifier for the operations internal tracking. This permits the user of the API to determine what a repeated call looks like.
Examples
We do a normal update call but setting the ClientRequestIdentifier parameter to the empty string so coreBOS can do the internal control of the operation. The description field is updated.
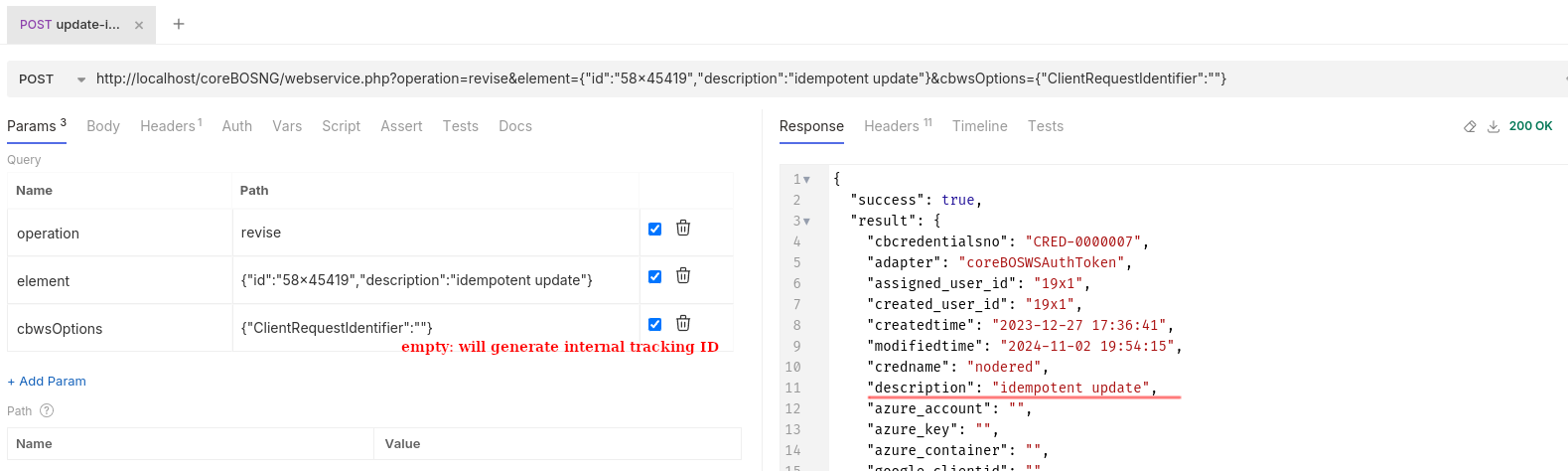
Now we update the description field from inside the application
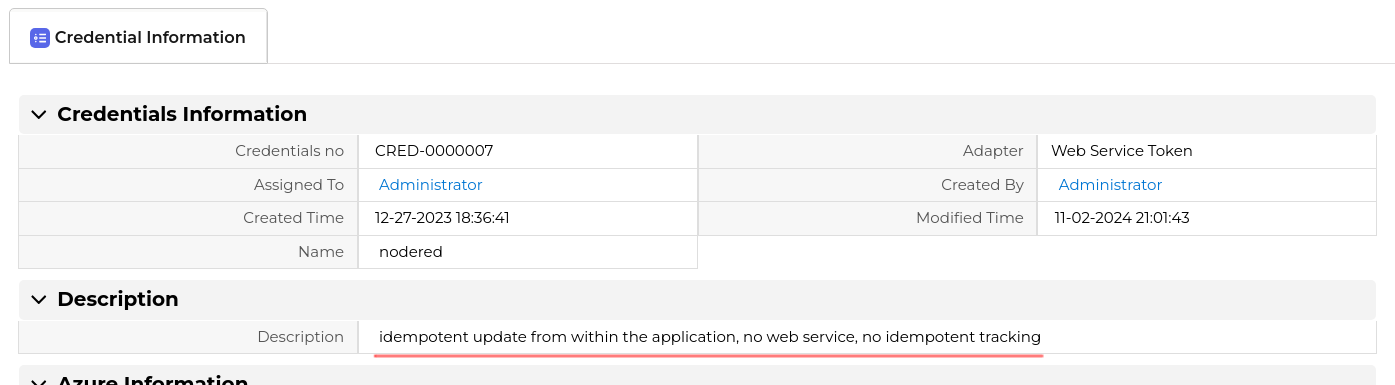
We do the call again and get the exact same result as the first call. The description field is NOT updated, the web service update call was detected as already executed and ignored.
References
- Making retries safe with idempotent APIs
- Idempotent Writes to Delta Lake Tables
- How to make data pipelines idempotent · Start Data Engineering
- Building Resilient Systems with Idempotent APIs - DEV Community
Next| Chapter 15: coreBOS Web Service Developer Tool.