The Master Detail Mapping in coreBOS allows you to establish a hierarchical relationship between two modules, where one module serves as the master and the other as the detail. This mapping defines the behavior and functionality associated with the master-detail relationship, such as record creation, deletion, visibility, and data synchronization.
To create a master-detail relationship between two modules, you need to define a Master Detail Mapping using XML configuration. The accepted format for the Master Detail Mapping is as follows:
<map>
<mastermodule>MasterModuleName</mastermodule>
<detailmodule>DetailModuleName</detailmodule>
<relationname>relation_name</relationname>
<detailfields>
<field>
<fieldname>fieldname</fieldname>
<mandatory>0|1</mandatory>
<edit>0|1</edit>
<quickcreate>0|1</quickcreate>
</field>
...
</detailfields>
<relationfields>
<field>
<masterfield>MasterFieldName</masterfield>
<detailfield>DetailFieldName</detailfield>
</field>
...
</relationfields>
</map>The <map> element represents the Master Detail Mapping. Within the <map> section, you specify the following elements:
<mastermodule>: Specifies the name of the master module.<detailmodule>: Specifies the name of the detail module.<relationname>: Specifies the name of the relationship between the master and detail modules.<detailfields>: Contains a list of<field>elements that define the fields in the detail module associated with the master-detail relationship. Each<field>element includes the<fieldname>,<mandatory>,<edit>, and<quickcreate>tags to define the field behavior.<relationfields>: Contains a list of<field>elements that define the mapping between fields in the master and detail modules. Each<field>element includes the<masterfield>and<detailfield>tags to specify the corresponding fields in the master and detail modules.
By configuring the Master Detail Mapping, you establish the relationship between the master and detail modules, define the fields and their behavior in the detail module, and specify the mapping between corresponding fields in the master and detail modules.
The Master Detail Mapping in coreBOS enables you to create a structured and hierarchical data model, allowing you to manage related records, enforce data integrity, and maintain data consistency across modules. It provides a powerful mechanism for organizing and manipulating data within your coreBOS application.
The inventory modules are examples of master-detail modules, there is a first section of "header" data followed by a set of lines that depend on it (product lines in this case).
With this mapping we can specify:
- the relationship between parent and child modules
- the fields that we should show in the list and detail view of the dependent module. if the field is a coreBOS field, the internal fieldID and column name will be returned with the map definition
- the aggregation fields that need to be calculated and shown
The full syntax of the map looks like this:
<map>
<originmodule>Master Module</originmodule>
<targetmodule>Detail Module</targetmodule>
<linkfields>
<originfield>id field of the master module</originfield>
<targetfield>id field of the detail module</targetfield>
</linkfields>
<sortfield>sequence field on the detail module to sort the records</sortfield>
<toolbar>
<title>translatable label of the header bar of the detail section</title>
<icon>standard-sprite/svg/symbols.svg#opportunity</icon>
<expandall>1</expandall> if an expand all button is present
<create>1</create> if an add button is present
</toolbar>
<listview>
<datasource>URL to get the rows to show</datasource>
<toolbar>
<moveup>1</moveup> if a move up button is present on the line
<movedown>1</movedown> if a move down button is present on the line
<delete>1</delete> if the records can be deleted from the list view
<edit>1</edit> if the records can be edtted from the list view
</toolbar>
<fields>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos.related</fieldtype>
<fieldname>...</fieldname>
<linkedto>...</linkedto>
<editable>0</editable>
<mandatory>0</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<editor></editor> type of editor to show in the inline edit of the cells
<sortable></sortable> if the column is sortable
<sortingType></sortingType> default direction of sort
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>codigo</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<editor></editor>
<sortable></sortable>
<sortingType></sortingType>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>cantidad</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<editor></editor>
<sortable></sortable>
<sortingType></sortingType>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>tipodescuento</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<editor></editor>
<sortable></sortable>
<sortingType></sortingType>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>descuento</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<editor></editor>
<sortable></sortable>
<sortingType></sortingType>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>dtomontante</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<editor></editor>
<sortable></sortable>
<sortingType></sortingType>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>linetotal</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<editor></editor>
<sortable></sortable>
<sortingType></sortingType>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
</fields>
</listview>
<detailview>
<layout></layout>
<fields>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos.related</fieldtype>
<fieldname>...</fieldname>
<linkedto>codigo</linkedto>
<editable>0</editable>
<mandatory>0</mandatory>
<defaultvalue>0</defaultvalue>
<duplicatevalue>0</duplicatevalue>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>codigo</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>cantidad</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>tipodescuento</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>descuento</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<layout></layout>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>linetotal</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
<position>top</position>
<currency>true</currency>
<layout></layout>
</field>
</fields>
</detailview>
<aggregations>
<operation>
<type>aggregation</type>
<items>callresponse</items>
<operation>count</operation>
<column>linetotal</column>
<variable>dqcilinesnum</variable>
<label>NumLines</label>
<position>top</position>
</operation>
<operation>
<type>aggregation</type>
<items>callresponse</items>
<operation>sum</operation>
<column>linetotal</column>
<variable>dqcilinestotal</variable>
<label>SumTotal</label>
<position>top</position>
<currency>true</currency>
</operation>
<operation>
<type>aggregation</type>
<items>callresponse</items>
<operation>sum</operation>
<column>dtomontante</column>
<variable>dqcidescuento</variable>
<label>SumDiscount</label>
<position>left</position>
<currency>true</currency>
</operation>
</aggregations>
</map>Other information returned with the map
Besides the information introduced in the map, the programmer will also get:
- mapnameraw the map name
- mapname the map name with no spaces nor special characters in lower case (for HTML ID)
- arrays of fields
- viewfields fieldIDs of the fields to show
- viewfieldnames names of the fields to show
- editfields fieldIDs of the fields to edit
- editfieldnames names of the fields to edit
- targetmoduleidfield the corebos module ID field for the Detail module
Inventory type Master-Details need an interface like this:
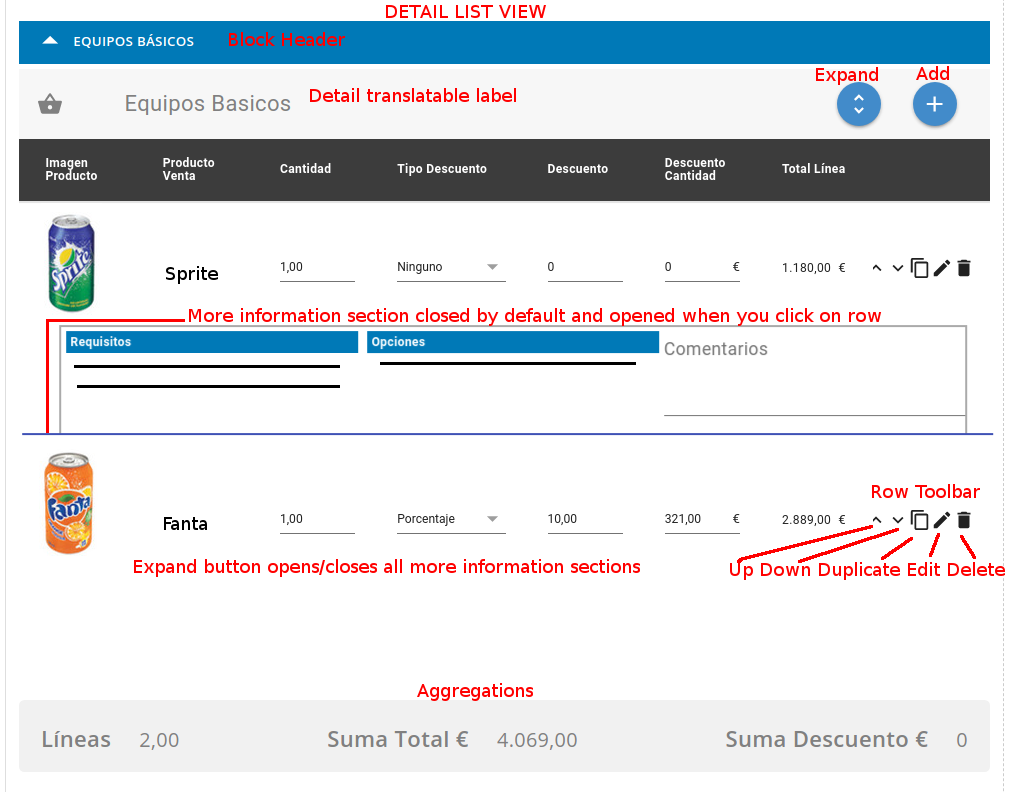
Support/History type Master-Details need an interface like this:
Generic Master Detail
This map can be used as infrastructure for you to create your own editor, but coreBOS will give you a generic editor if you create the map between two modules with a one-to-many (1:m) relation and create the necessary map and actions.
For this to work, we have to follow some rules and set up two actions.
- In the business map record, the target module picklist field MUST be the detail module
- The sortfield MUST be an integer
- You must create a business action with the Master-Detail widget, something like this
block://MasterDetailGridLayoutWidget:modules/Utilities/MasterDetailGridLayoutWidget.php:PID=$RECORD$&mapname=Project-ProjectTaskThe link type is DETAILVIEWWIDGET and the module it is on has to be the Master module (Projects in the example above)
- You must create a business action that loads the Master-Detail javascript code, something like this
include/js/masterdetailgrid.jsThe link type is HEADERSCRIPT and the module it is on has to be the Master module (Projects in the example above)
- List view datasource: the special value corebos means that the detail is a normal coreBOS module
- icon: in the header of the master-detail block we follow the LDS guidelines and prefix the title with an icon if given here. You can select any valid icon from LDS
Read about the Making of the Generic Editor
Master Detail on Inventory Modules
There is a special implementation where this mapping can be used. The four existing inventory modules will look for specific master-detail mapping with the InventoryDetail module and, if found, they will permit you to edit fields on that module in the product lines. This makes it easy to track a serial number, add an expiration date, track units served, or calculate costs for each line.
As usual with Business Mappings the name is the means that the system uses to detect the ones to apply and, in this case, the name must be {ModuleName}InventoryDetails
Here is a Master-Detail mapping for the PurchaseOrder module (PurchaseOrderInventoryDetails) that will permit you to edit units_delivered_received, a custom field and the product cost:
<map>
<originmodule>PurchaseOrder</originmodule>
<targetmodule>InventoryDetails</targetmodule>
<linkfields>
<originfield>lineitem_id</originfield>
<targetfield>lineitem_id</targetfield>
</linkfields>
<sortfield>sequence_no</sortfield>
<detailview>
<fields>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>units_delivered_received</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>cf_795</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
</field>
<field>
<fieldtype>corebos</fieldtype>
<fieldname>cost_price</fieldname>
<editable>1</editable>
<mandatory>1</mandatory>
<hidden>0</hidden>
</field>
</fields>
</detailview>
</map>See this video for a demonstration:
Next | Chapter 11: IOMap.