The coreBOS Decision Table Mapping is a powerful feature that allows you to define complex business rules and automate decision-making processes within the coreBOS application. The mapping provides a structured and configurable way to define conditions, actions, and outcomes based on specific criteria.
The general idea comes from the Decision Model and Notation (DMN) structure used in BPM but very adapted to the specific coreBOS environment and infrastructure.
You can find a few useful links about DMN here:
- DMN Tutorial
- DMN Tutorial PDF
- Decision Table Reference
- Decision Table Constructor
- Decision Table Constructor
- https://www.omg.org/spec/DMN/
By defining decision rules using the Decision Table Mapping, you can automate various processes within coreBOS based on specific conditions. For example, you can define rules to automatically update field values, assign records to specific users, trigger notifications, or perform custom actions.
The flexibility of the Decision Table Mapping allows you to create complex decision-making logic with multiple conditions, actions, and outcomes. This feature empowers you to streamline and automate your business processes, reducing manual intervention and ensuring consistent and efficient decision-making within the coreBOS application.
Decision Table Map Format
The accepted format for this map is basically a set of rules which can be of three types:
- Expressions
- Condition Expression or Condition Query business map names/IDs
- Decision Tables
Expressions
Expressions contain any workflow expression that can be evaluated in the context of the Decision Map. These are exactly like Condition Expression maps but written directly inside this business map.
Business Map Name/ID
This type is simply the name or CRMID of any existing Condition Expression or Condition Query business map, they will be loaded and evaluated in the context of the Decision Map
Decision Tables
This type expects to have the values to search on inside a coreBOS module.
We will be able to define the conditions to filter the records in the module and then a set of search conditions to look for records.
Full Map Structure
<decision>
<hitPolicy></hitPolicy> <!-- U F C A R G -->
<aggregate></aggregate> <!-- only available if hitPolicy=G: sum,min,max,count -->
<rules>
<rule>
<sequence></sequence>
<expression></expression>
<output></output> <!-- ExpressionResult, FieldValue, crmObject, Row -->
</rule>
<rule>
<sequence></sequence>
<mapid></mapid>
<output></output> <!-- ExpressionResult, FieldValue, crmObject, Row -->
</rule>
<rule>
<sequence></sequence>
<decisionTable>
<module></module>
<conditions> <!-- QueryGenerator conditions -->
<condition>
<input></input> <!-- context variable name -->
<operation></operation> <!-- QueryGenerator operators -->
<field></field> <!-- fieldname of module -->
</condition>
</conditions>
<orderby></orderby> <!-- column to order the records by -->
<searches>
<search>
<condition>
<input></input> <!-- context variable name -->
<preprocess></preprocess> <!-- optional: if present, the result of the expression it contains will be used as the input -->
<operation></operation> <!-- QueryGenerator operators -->
<field></field> <!-- fieldname of module -->
</condition>
</search>
</searches>
<output></output> <!-- fieldname or fieldnames separated by commas or star (*) for all fields -->
</decisionTable>
<output></output> <!-- ExpressionResult, FieldValue, crmObject, Row -->
</rule>
</rules>
</decision>Hit Policy
- Unique: Only a single rule can be satisfied. The decision table result contains the output entries of the satisfied rule. If more than one rule is satisfied, the Unique hit policy is violated.
- First: Multiple rules can be satisfied. The decision table result contains only the output of the first satisfied rule.
- Collect: Multiple rules can be satisfied. The decision table result contains the output of all satisfied rules in an arbitrary order as a list.
- Any: Multiple rules can be satisfied. However, all satisfied rules must generate the same output. The decision table result contains only the output of one of the satisfied rules. If multiple rules are satisfied which generate different outputs, the hit policy is violated.
- RuleOrder: Multiple rules can be satisfied. The decision table result contains the output of all satisfied rules in the order of the rules in the decision table.
- aGgregate:
- The SUM aggregator sums up all outputs from the satisfied rules.
- The MIN aggregator can be used to return the smallest output value of all satisfied rules.
- The MAX aggregator can be used to return the largest output value of all satisfied rules.
- The COUNT aggregator can be used to return the count of satisfied rules.
Read the DMN Hit Policy reference
Output Options
- ExpressionResult: whatever the expression returns will be returned
- FieldValue: we understand that the expression returns a field name which we will evaluate in the given context
- crmObject: we understand that the expression returns a CRM ID so we instantiate the module and return the fully-loaded object
- Row: will return the full row of fields indicated in the "output" directive
Execution
To execute a decision map and get the result we use the coreBOS Rules service. coreBOS Rule will see that the given map is actually a decision table and will evaluate the map with the given context.
$result = coreBOS_Rule::evaluate(put your decision map ID or name here, $context);
Web service execution
You can evaluate Decision Maps via the web service endpoint: cbRule
$context = array(
'guestcount' => '4',
'season' => 'Winter',
);
$context = json_encode($context);
$mapid = 'SeasonDish twocolumns';
//sessionId is obtained from loginResult.
$params = "sessionName=$cbSessionID";
$params.= "&operation=cbRule";
$params.= "&conditionid=".urlencode($mapid);
$params.= "&context=".urlencode($context);
//Retrieve must be GET Request.
$response = $httpc->fetch_url("$cbURL?$params");
$dmsg.= debugmsg("Raw response (json)", $response);
//decode the json encode response from the server.
$jsonResponse = json_decode($response, true);
$dmsg.= debugmsg("Webservice response", $jsonResponse);
//operation was successful get the token from the response.
if($jsonResponse['success']==false) {
$dmsg.= debugmsg('failed:'.$jsonResponse['error']['message']);
echo 'rule failed!';
} else {
echo $jsonResponse['result'];
}Examples
Select Dish with Expressions
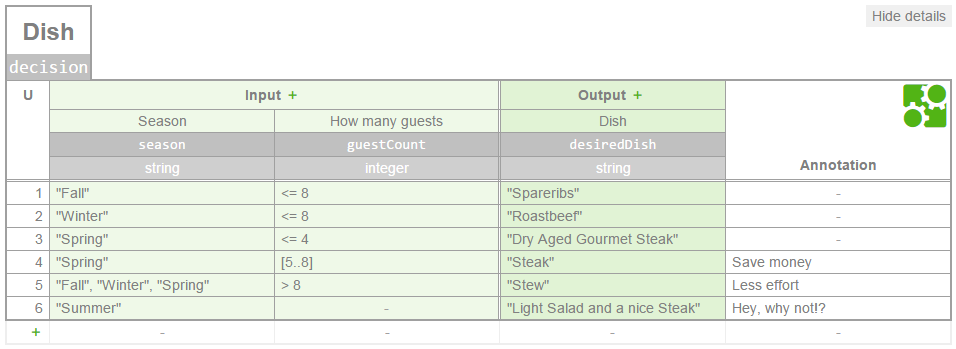
<decision>
<hitPolicy>U</hitPolicy>
<rules>
<rule>
<sequence>1</sequence>
<expression><![CDATA[if AND('$[season]'=='Fall', $[guestcount]<=8) then 'Spareribs' else '__DoesNotPass__' end]]></expression>
<output>ExpressionResult</output>
</rule>
<rule>
<sequence>2</sequence>
<expression><![CDATA[if AND('$[season]'=='Winter', $[guestcount]<=8) then 'Roastbeef' else '__DoesNotPass__' end]]></expression>
<output>ExpressionResult</output>
</rule>
<rule>
<sequence>3</sequence>
<expression><![CDATA[if AND('$[season]'=='Spring', $[guestcount]<=4) then 'Dry Aged Gourmet Steak' else '__DoesNotPass__' end]]></expression>
<output>ExpressionResult</output>
</rule>
<rule>
<sequence>4</sequence>
<expression><![CDATA[if AND('$[season]'=='Spring', AND($[guestcount]>=5, $[guestCount]<=8)) then 'Steak' else '__DoesNotPass__' end]]></expression>
<output>ExpressionResult</output>
</rule>
<rule>
<sequence>5</sequence>
<expression><![CDATA[if AND(OR('$[season]'=='Fall', OR('$[season]'=='Winter', '$[season]'=='Spring')), $[guestcount]>8) then 'Stew' else '__DoesNotPass__' end]]></expression>
<output>ExpressionResult</output>
</rule>
<rule>
<sequence>6</sequence>
<expression><![CDATA[if '$[season]'=='Summer' then 'Light Salad and a nice Steak' else '__DoesNotPass__' end]]></expression>
<output>ExpressionResult</output>
</rule>
</rules>
</decision>Select Dish with Module

Let's suppose we have a module called DecisionConditions with these fields:
- sequence
- season
- guestcountmin
- guestcountmax
- desireddish
and these records
| sequence | season | guestcountmin | guestcountmax | desireddish |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fall | 0 | 8 | Spareribs |
| 2 | Winter | 0 | 8 | Roastbeef |
| 3 | Spring | 0 | 4 | Dry Aged Gourmet Steak |
| 4 | Spring | 5 | 8 | Steak |
| 5 | Fall | 9 | 10000 | Stew |
| 6 | Winter | 9 | 10000 | Stew |
| 7 | Spring | 9 | 10000 | Stew |
| 8 | Summer | 0 | 10000 | Light Salad and a nice Steak |
<decision>
<hitPolicy>U</hitPolicy>
<rules>
<rule>
<sequence>1</sequence>
<decisionTable>
<module>DecisionConditions</module>
<orderby>sequence</orderby> <!-- column to order the records by -->
<searches>
<search>
<condition>
<input>season</input> <!-- context variable name -->
<operation>e</operation> <!-- QueryGenerator operators -->
<field>season</field> <!-- fieldname of module -->
</condition>
<condition>
<input>guestcount</input> <!-- context variable name -->
<operation>ge</operation> <!-- QueryGenerator operators -->
<field>guestcountmin</field> <!-- fieldname of module -->
</condition>
<condition>
<input>guestcount</input> <!-- context variable name -->
<operation>le</operation> <!-- QueryGenerator operators -->
<field>guestcountmax</field> <!-- fieldname of module -->
</condition>
</search>
</searches>
<output>desireddish</output> <!-- fieldname -->
</decisionTable>
<output>FieldValue</output>
</rule>
</rules>
</decision>In the example above I decided to add two columns for the Guest Count, in order to convert the range [5..8] into two records. In this mindset, I also use the value 10000 as an "infinite" value.
But the truth is that as the implementor of both the decision table map and module I have full control of how I want my users to define the conditions. Let's suppose that I want the users of the module to be able to define the condition with only one column for guest count like is reflected in the image. In this case, I would have implemented a module with these fields:
- sequence
- season
- guestcount
- desireddish
these records
| sequence | season | guestcount | desireddish |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fall | 8 | Spareribs |
| 2 | Fall | 10000 | Stew |
| 3 | Spring | 4 | Dry Aged Gourmet Steak |
| 4 | Spring | 8 | Steak |
| 5 | Spring | 10000 | Stew |
| 5 | Winter | 8 | Roastbeef |
| 6 | Winter | 10000 | Stew |
| 7 | Summer | 10000 | Light Salad and a nice Steak |
and this map
<decision>
<hitPolicy>F</hitPolicy>
<rules>
<rule>
<sequence>1</sequence>
<decisionTable>
<module>DecisionConditions</module>
<orderby>sequence</orderby> <!-- column to order the records by -->
<searches>
<search>
<condition>
<input>season</input> <!-- context variable name -->
<operation>e</operation> <!-- QueryGenerator operators -->
<field>season</field> <!-- fieldname of module -->
</condition>
<condition>
<input>guestcount</input> <!-- context variable name -->
<operation>le</operation> <!-- QueryGenerator operators -->
<field>guestcount</field> <!-- fieldname of module -->
</condition>
</search>
</searches>
<output>desireddish</output> <!-- fieldname -->
</decisionTable>
<output>FieldValue</output>
</rule>
</rules>
</decision>In this case, I am playing with the Hit Policy which has changed to First, so now my users must understand that the ranges are defined from the previous value to the one defined in each record and that sequence is VERY important.
Since, in the end, the supported operations are those of the Query Generator, which even supports ranges:
QueryGenerator->addConditions(column, operator, values)
where operator can be '[]', '[[', ']]', '][' among many othersthe possibilities that the implementor has are very big.
IGNORE Reserved Word
Finally, comment on a very important option where you can set the value of any variable in the context to __IGNORE__ to have that variable eliminated from the decision. This permits us to create complex rules with many variables where we search on only a few of them at a time.
We can also use this special reserved word in the rules table itself to create rules which cover many cases. For example, we could have a table of rules like this:
| input1 | input2 | output |
|---|---|---|
| e1 | c1 | r1 |
| __IGNORE__ | c2 | r2 |
| e3 | c3 | r3 |
With these rules in place, any decision that has input2==c2 will pass no matter what value is passed in as input1. Note that this can easily cause that more than one rule to pass. If we add a rule to the table above, like this:
| input1 | input2 | output |
|---|---|---|
| e1 | c1 | r1 |
| __IGNORE__ | c2 | r2 |
| e2 | c2 | r2b |
| e3 | c3 | r3 |
and we pass in the values
- input1=e2
- input2=c2
both r2 and r2b will pass and be returned, so if we have a hit policy of Unique it will fail and if we have a hit policy of First then the sequence is of utmost importance to get the correct result.
Default Value
Using the __IGNORE__ reserved word we can implement a default value for our rules. If we define a rule where all the input values are set to __IGNORE__, this rule will pass for all input values. If we set the hit policy of the decision map to First and order the rules in a way that the all __IGNORE__ rule is always the last to be evaluated we accomplish a decision table where any combination of input values that is not explicitly defined will return the values in the all __IGNORE__ rule instead of __DoesNotPass__
Preprocess Directive
Following the new enhancements, we don't have to valorize context variables on the Decision Table map using the Execute Expression Workflow before evaluating the Decision table map. The map will be evaluated on the context of the values that are present on the screen.
But there may be cases where we don’t want the context variable to hold the entire value of the field. Here comes in play the preprocess directive. The preprocess directive is optional. That being said, if it is present it will send its value to the workflow expression system, get back the result and use that result to search the Decision Table Module. If you think about it the preprocess directive carries the work of the Execute Expression workflow task. You don’t need to explicitly use the workflow system because the preprocess directive will "call" it for you.
Example:
Let's change the logic we had in the last example above.
Remove all the records with the season of Spring and add this new rule on the decision table module: If the season is Spring then regardless of how many guests there are I want the desired dish to be Beef.
That would be a record like this in the decision table module.
| sequence | season | guestcount | desireddish |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fall | 8 | Spareribs |
| 2 | Fall | 10000 | Stew |
| 3 | Spring | * | Beef |
| 5 | Winter | 8 | Roastbeef |
| 6 | Winter | 10000 | Stew |
| 7 | Summer | 10000 | Light Salad and a nice Steak |
Lets see how that will look on our Decision Table map:
<condition>
<input>guestcount</input> <!-- context variable name -->
<preprocess>if '$[season]' == 'Spring' then '*' else '$[guestcount]' end</preprocess> <!-- if present sends the expression to the workflow expression system-->
<operation>e</operation> <!-- QueryGenerator operators -->
<field>guestcount</field> <!-- fieldname of module -->
</condition>As you can see we are using the preprocess directive. What is inside the preprocess directive will be sent to the workflow system.
So if the season is Spring that valorizes the context variable with the value * and then searches the decision table module for a match. Now, whenever the decision map gets evaluated on a record whose value of the Season field is Spring it will consider the value of Guest Number as * and for our Decision Table module that means that the desired dish is Beef.
Select Global Variable Escalation
A decision map that would return the value of a global variable would look something like the map below. The context would have to send in all the role and group of the current user and I'm not totally sure if the "module list" would work as it is below, but it will be VERY close and enough for you to get an idea of how this map works.
<decision>
<hitPolicy>F</hitPolicy>
<rules>
<rule>
<sequence>1</sequence>
<decisionTable>
<module>GlobalVariable</module>
<searches>
<search> <!-- Mandatory GV -->
<condition>
<input>gvname</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>gvname</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>checkboxtrue</input> <!-- checkboxtrue == 1 in context -->
<operation>e</operation>
<field>mandatory</field>
</condition>
</search>
<search> <!-- In module for user -->
<condition>
<input>gvname</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>gvname</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>userid</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>assigned_user_id</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>checkboxtrue</input> <!-- checkboxtrue == 1 in context -->
<operation>e</operation>
<field>inmodulelist</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>gvmodule</input>
<operation>c</operation>
<field>gvmodule</field>
</condition>
</search>
<search> <!-- In module for group -->
<condition>
<input>gvname</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>gvname</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>groupid</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>assigned_user_id</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>checkboxtrue</input> <!-- checkboxtrue == 1 in context -->
<operation>e</operation>
<field>inmodulelist</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>gvmodule</input>
<operation>c</operation>
<field>gvmodule</field>
</condition>
</search>
<search> <!-- In module for role -->
<condition>
<input>gvname</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>gvname</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>userrole</input>
<operation>c</operation>
<field>gvrole</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>checkboxtrue</input> <!-- checkboxtrue == 1 in context -->
<operation>e</operation>
<field>inmodulelist</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>gvmodule</input>
<operation>c</operation>
<field>gvmodule</field>
</condition>
</search>
<search> <!-- without module for user -->
<condition>
<input>gvname</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>gvname</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>userid</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>assigned_user_id</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>checkboxfalse</input> <!-- checkboxfalse == 0 in context -->
<operation>e</operation>
<field>inmodulelist</field>
</condition>
</search>
<search> <!-- without module for group -->
<condition>
<input>gvname</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>gvname</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>groupid</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>assigned_user_id</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>checkboxfalse</input> <!-- checkboxfalse == 1 in context -->
<operation>e</operation>
<field>inmodulelist</field>
</condition>
</search>
<search> <!-- without module for role -->
<condition>
<input>gvname</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>gvname</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>userrole</input>
<operation>c</operation>
<field>gvrole</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>checkboxfalse</input> <!-- checkboxfalse == 1 in context -->
<operation>e</operation>
<field>inmodulelist</field>
</condition>
</search>
<search> <!-- Default GV -->
<condition>
<input>gvname</input>
<operation>e</operation>
<field>gvname</field>
</condition>
<condition>
<input>checkboxtrue</input> <!-- checkboxtrue == 1 in context -->
<operation>e</operation>
<field>default</field>
</condition>
</search>
</searches>
<output>value</output> <!-- fieldname -->
</decisionTable>
<output>FieldValue</output>
</rule>
</rules>
</decision>Next | Chapter 21: REST/SOAP call and retrieval.